Prediction of Intrinsic Transcription Termination Sites in Bacteria
We designed the INTERPIN (INtrinsic transcription TERmination hairPIN) algorithm to predict Intrinsic transcription terminators in bacterial genomes. The INTERPIN database here contains predictions on 12745 bacterial genomes where hairpins have been identified by the program. It is the largest collection of predicted intrinsic terminators to date with approximately 25,000,000 hairpins.
Through the INTERPIN program, we have found a new type of hairpins termed as cluster hairpins. Here two or more hairpins work in tandem to cause termination and might even have higher efficiency than the sum of individual termination efficiencies. The hairpins in a cluster are present at <15 bases from each other.
In the database, the bacterial genomes have been organised into respective phyla or can be searched by their name as well as NCBI ID. In each bacterial prediction, the users can gain information on the predicted operons, frequency of cluster and single hairpin and their distance from the stop codon. Raw information about all hairpin predictions including their location, energies, etc. can also be downloaded (see help).
To aid the visualization of hairpins, an IGV visualizer has been added for each genome.
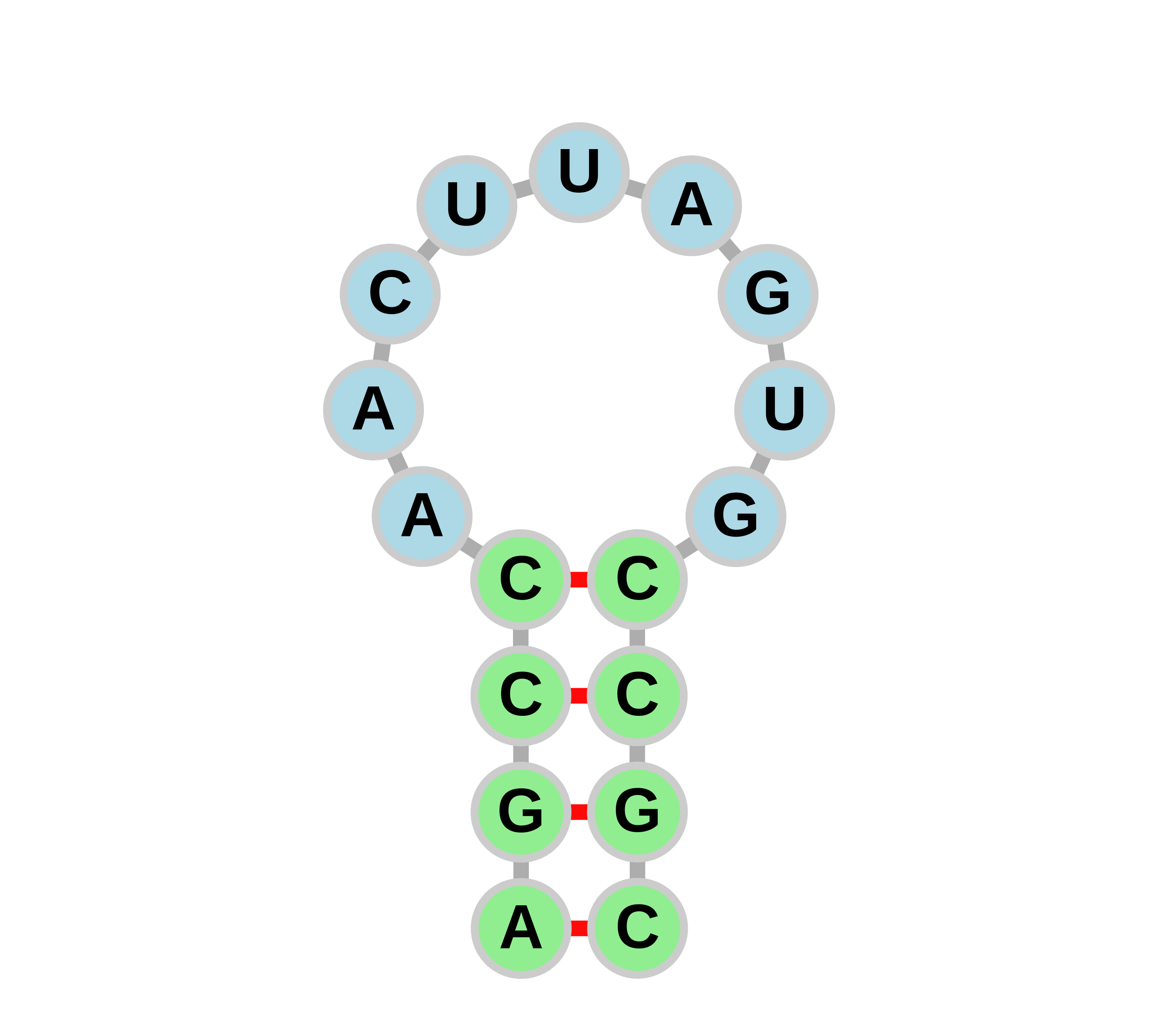
Users can view and interact with the predicted hairpins, operons and corresponding gene annotations here. Hairpin secondary and tertiary structures can also be viewed (see help), along with other features.
Further description and examples are provided in the “Help” section to provide users more details of features available in the database.